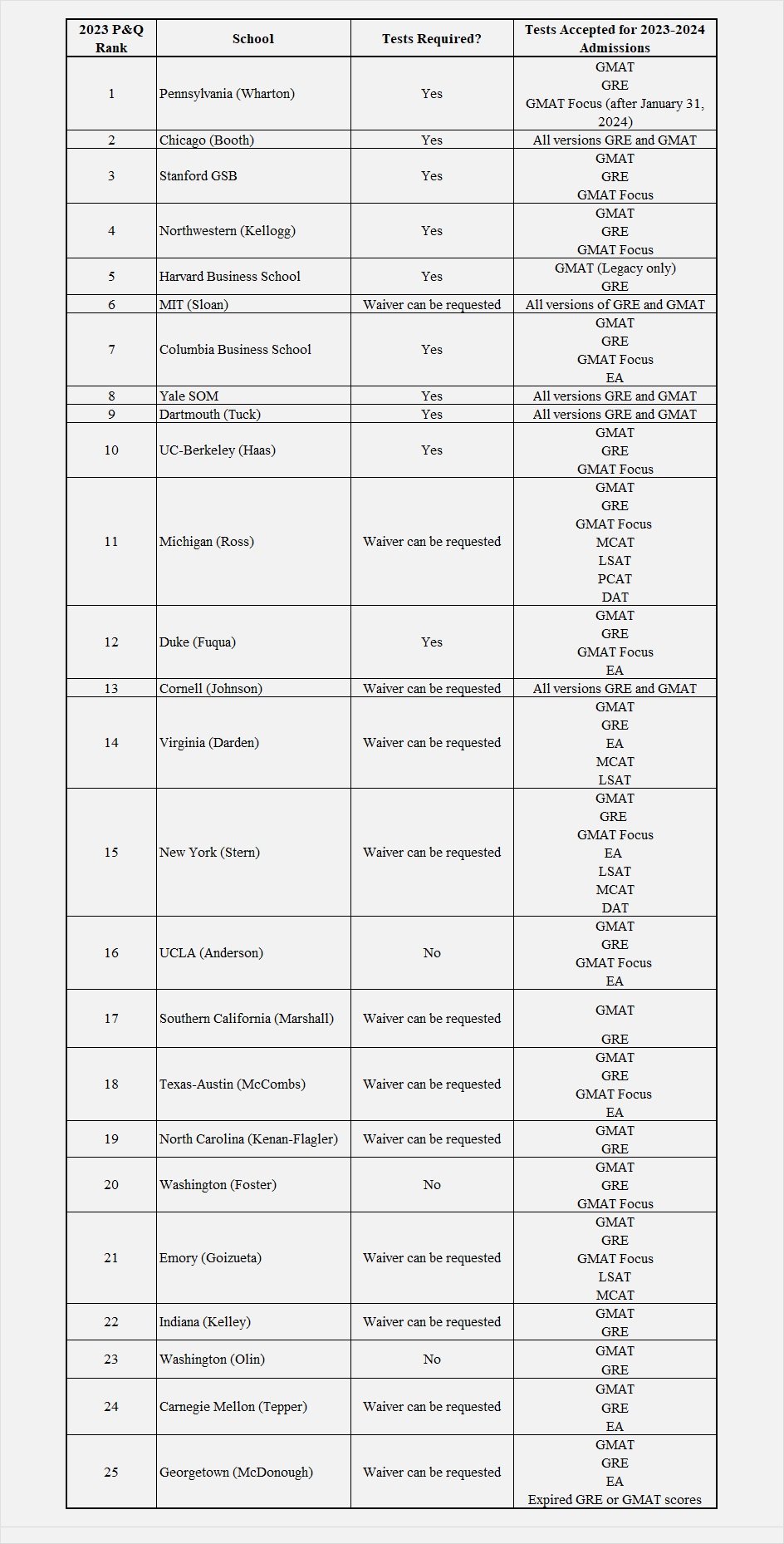
In the world of MBA Admissions, standardized testing has become a lot less, well, standard. Admissions committees used to accept only the GMAT and/or GRE, but more options have opened up in the post-pandemic era including test waivers for past academic or professional performance, and a wider range of accepted tests including the Executive Assessment (EA) and even the MCAT or LSAT.
The EA is a 90-minute exam, requires minimal preparation, and has historically been used for EMBA admissions. It is a good choice for applicants to full-time MBA programs who have already demonstrated strong quantitative skills through prior academic or professional experiences Today, even some elite schools such as Columbia, Duke Fuqua, and Michigan Ross are allowing students to submit EA scores in lieu of GRE and GMAT scores.
In addition to the EA, some schools like Virginia’s Darden and NYU Stern are accepting LSAT, MCAT, and Dental Admission Test (DAT) scores. Others, like Georgetown McDonough, will allow applicants to submit expired GRE and GMAT scores. And many top ranked MBA programs are open to accepting the scores from the shorter versions of the GRE and GMAT exams. Chicago Booth, Stanford GSB, and Northwestern Kellogg will all allow applicants to submit GMAT Focus results this year.
Harvard Business School is one of the few schools that have pointedly said they will not accept GMAT Focus scores for 2023-2024 admissions. And Wharton will accept GMAT Focus test scores dated January 31, 2024 or later, when the GMAT Focus has been merged with the legacy GMAT.
The chart below shows the standardized tests that each school’s full-time two-year MBA program will accept in 2023-2024. Please note that some schools have not yet commented on when they will start to accept GMAT Focus scores.